क्या आपने कभी सोचा है कि जब आप बालों से कंघी करते हैं तो छोटे कागज़ के टुकड़े कंघी की तरफ क्यों आकर्षित होते हैं? या फिर सर्दियों में जब आप ऊनी कपड़े पहनते हैं तो क्यों आपको हल्का झटका लगता है? ये सभी घटनाएं विद्युत आवेश और क्षेत्र की अद्भुत दुनिया का हिस्सा हैं!
आज का यह लेख आपको Class 12 Physics के सबसे महत्वपूर्ण अध्याय “विद्युत आवेश और क्षेत्र” की गहरी समझ देगा। डरने की कोई बात नहीं है – हम साथ मिलकर इस fascinating topic को step-by-step explore करेंगे!
Chapter Overview: आपको क्या सीखने को मिलेगा?
इस अध्याय में हम निम्नलिखित महत्वपूर्ण topics cover करेंगे:
- विद्युत आवेश की प्रकृति और गुण
- कूलॉम का नियम (Coulomb’s Law)
- विद्युत क्षेत्र (Electric Field)
- विद्युत क्षेत्र रेखाएं (Electric Field Lines)
- विद्युत द्विध्रुव (Electric Dipole)
- गॉस का नियम (Gauss’s Law)

विद्युत आवेश क्या है? – समझिए आसान भाषा में!
मूल अवधारणा (Basic Concept)
विद्युत आवेश प्रकृति की सबसे fundamental properties में से एक है। यह matter का वह intrinsic property है जो electromagnetic interactions को जन्म देती है।
परिभाषा:
विद्युत आवेश (Electric Charge) पदार्थ का वह मूलभूत गुण है, जिसके कारण वह विद्युत और चुंबकीय बल उत्पन्न करता है और अनुभव करता है।
Real-life Example: जब आप प्लास्टिक के पैन को सूखे कपड़े से रगड़ते हैं, तो पैन पर विद्युत आवेश आ जाता है। इसीलिए यह छोटे कागज़ के टुकड़ों को अपनी तरफ आकर्षित करता है!
आवेश के मुख्य गुण (Properties of Electric Charge)
1. द्विध्रुवीय प्रकृति (Bipolar Nature)
- धनात्मक आवेश (+): प्रोटॉन में पाया जाता है
- ऋणात्मक आवेश (-): इलेक्ट्रॉन में पाया जाता है
2. आवेश का संरक्षण (Conservation of Charge)
“प्रकृति में आवेश न तो उत्पन्न होता है और न ही नष्ट होता है – यह केवल transfer होता है!”
Quick Reference Box:
आवेश संरक्षण नियम: Q(total) = Q₁ + Q₂ + Q₃ + ... = constant3. आवेश का परिमाणीकरण (Quantization of Charge)
- सभी आवेश elementary charge (e = 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ C) के integer multiples होते हैं
- Formula: Q = ne (where n = integer)
कूलॉम का नियम (Coulomb’s Law): Physics का Heart!
Charles-Augustin de Coulomb की खोज
1785 में Coulomb ने एक revolutionary discovery की थी! उन्होंने पाया कि दो point charges के बीच force का mathematical relationship है।
कूलॉम नियम का Statement
“दो point charges के बीच लगने वाला विद्युतस्थैतिक बल दोनों आवेशों के गुणनफल के समानुपाती और उनके बीच की दूरी के वर्ग के व्युत्क्रमानुपाती होता है।”
Mathematical Formula
F = k(q₁q₂)/r²Where:
- F = विद्युतस्थैतिक बल (N)
- k = कूलॉम स्थिरांक = 9 × 10⁹ Nm²/C²
- q₁, q₂ = आवेश (C)
- r = दूरी (m)

Vector Form में कूलॉम नियम
F⃗₁₂ = (1/4πε₀) × (q₁q₂/r²) × r̂₁₂
Where:
- ε₀ = permittivity of free space = 8.85 × 10⁻¹² C²/Nm²
- r̂₁₂ = unit vector from charge 1 to charge 2
Problem Solving Strategy
Step 1: Identify करें कि कौन सा charge कहां placed है
Step 2: Distance calculate करें
Step 3: Coulomb’s law apply करें
Step 4: Force की direction determine करें
Step 5: Vector addition करें (यदि multiple charges हों)
Sample Problem
प्रश्न: दो point charges q₁ = +3μC और q₂ = -2μC, 5 cm की दूरी पर स्थित हैं। उनके बीच का force calculate करें।
हल:
Given: q₁ = +3×10⁻⁶ C, q₂ = -2×10⁻⁶ C, r = 0.05 m
F = k(q₁q₂)/r²
F = (9×10⁹) × (3×10⁻⁶) × (2×10⁻⁶) / (0.05)²
F = 21.6 N (attractive force)आसान trick: Charges के signs opposite हैं, इसलिए force attractive होगी!
विद्युत क्षेत्र (Electric Field): Invisible Force का Map!
Electric Field का Concept
परिभाषा:
किसी बिंदु पर विद्युत क्षेत्र वह बल प्रति इकाई धनात्मक परीक्षण आवेश है, जो उस बिंदु पर लगाया जाता है।
“विद्युत क्षेत्र वह region है जहां कोई charged particle electromagnetic force experience करता है।”
Analogy: जैसे पृथ्वी के चारों ओर gravitational field होता है, वैसे ही charged objects के चारों ओर electric field होता है!
Mathematical Definition
E⃗ = F⃗/q₀
Where:
- E⃗ = Electric field vector (N/C or V/m)
- F⃗ = Force on test charge (N)
- q₀ = Test charge (C)
Point Charge का Electric Field
E⃗ = (1/4πε₀) × (Q/r²) × r̂
Key Points:
- Electric field की direction positive charge से away होती है
- Negative charge की तरफ electric field inward होती है
- Field का magnitude distance के साथ decrease होता है
Superposition Principle
“यदि multiple charges present हैं, तो net electric field सभी individual fields का vector sum होता है।”
E⃗net = E⃗₁ + E⃗₂ + E⃗₃ + …
Common Mistakes से बचें!
गलती: Electric field को scalar quantity मानना
सही: Electric field एक vector quantity है – direction important है!
गलती: Test charge का effect ignore करना
सही: Test charge infinitely small होना चाहिए
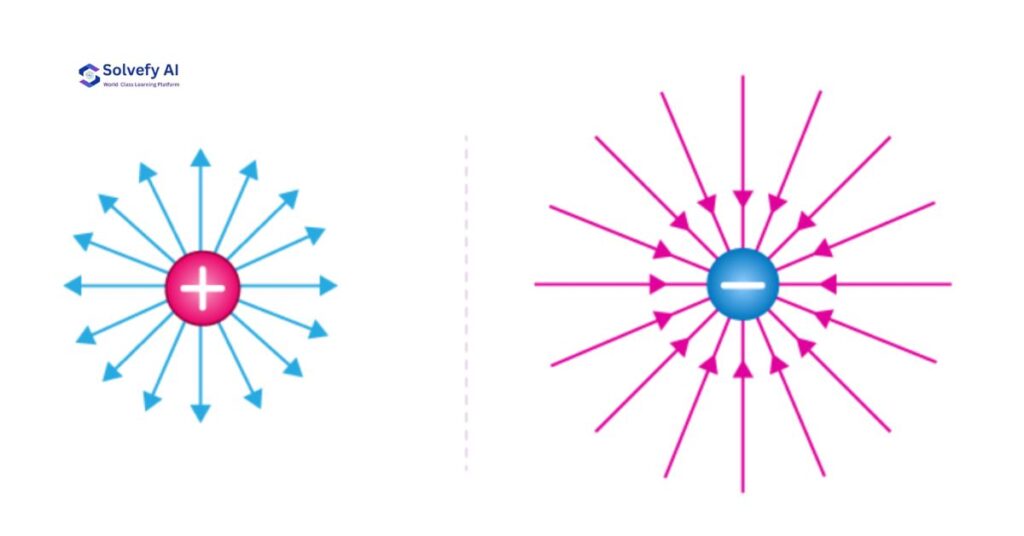
विद्युत क्षेत्र रेखाएं (Electric Field Lines): Visual Physics!
Field Lines क्या हैं?
Electric field lines एक graphical representation है जो electric field की direction और strength को visually show करती है।
Field Lines के नियम (Rules)
- Direction Rule: Field lines positive charge से negative charge की तरफ जाती हैं
- Tangent Rule: किसी भी point पर field line का tangent उस point पर electric field की direction देता है
- Density Rule: Field lines का density field की strength indicate करता है
- Non-intersecting Rule: Field lines कभी intersect नहीं करतीं

Different Configurations
1. Single Positive Charge
- Field lines radially outward
- Uniform distribution in all directions
2. Single Negative Charge
- Field lines radially inward
- Converging pattern
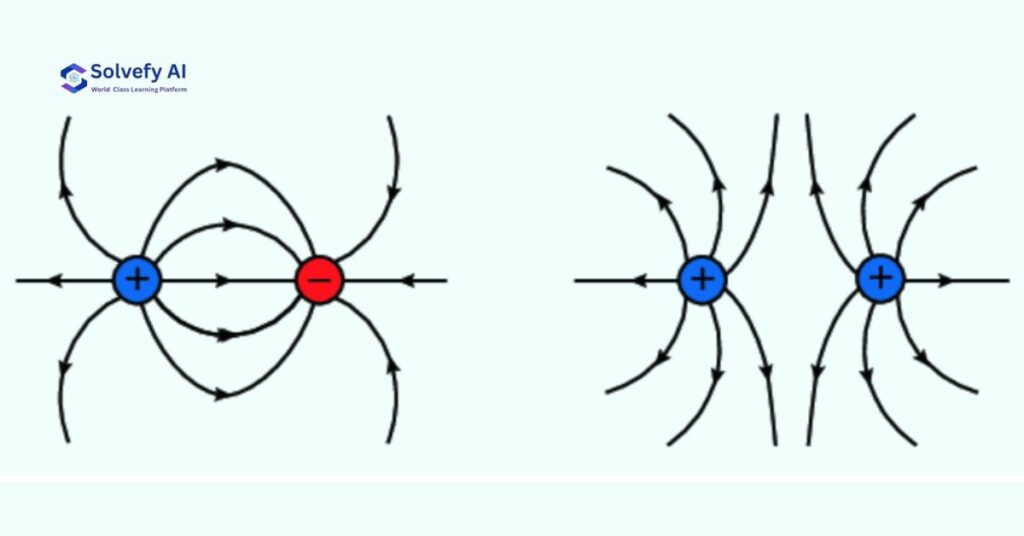
3. Electric Dipole
- Field lines start from positive, end at negative
- Beautiful curved pattern
4. Two Similar Charges
- Repulsive pattern
- No field lines between charges
Practical Applications
Real-world Example: Lightning rods का design electric field lines की concept पर based है! Sharp points पर field lines concentrate होती हैं, जिससे lightning easily discharge हो जाती है।
विद्युत द्विध्रुव (Electric Dipole): Nature का Balance!
Dipole की Definition
“दो equal और opposite charges जो small distance से separated हों, electric dipole कहलाते हैं।”
Dipole Moment
p⃗ = q × d⃗
Where:
- p⃗ = Electric dipole moment (C⋅m)
- q = Magnitude of charge (C)
- d⃗ = Distance vector from negative to positive charge (m)
Dipole in Uniform Electric Field
1. Force on Dipole
Net force = Zero (क्योंकि forces cancel out)
2. Torque on Dipole
τ⃗ = p⃗ × E⃗
τ = pE sin θ
Dipole की Field
Axial Position पर (along the axis):
E = (1/4πε₀) × (2p/r³) (for r >> a)
Equatorial Position पर (perpendicular):
E = (1/4πε₀) × (p/r³) (for r >> a)
Real-life Applications
क्या आप जानते हैं?
- Water molecules natural dipoles हैं!
- इसीलिए salt पानी में dissolve हो जाता है
- Microwave ovens भी dipole rotation का use करते हैं
Motivational Quote: “हर molecule में छुपी है एक छोटी कहानी – आवेशों के dance की, जो बनाती है life को possible!”
गॉस का नियम (Gauss’s Law): Symmetry की Power!
Gauss’s Law Statement
“किसी closed surface से गुजरने वाला total electric flux उस surface के अंदर enclosed charge के proportional होता है।”
Mathematical Form
∮ E⃗⋅dA⃗ = Q_enclosed/ε₀
Gauss’s Law के Applications
1. Infinite Line Charge
E = λ/(2πε₀r)
2. Infinite Plane Sheet
E = σ/(2ε₀)
3. Spherical Charge Distribution
- Inside: E = 0 (for hollow sphere)
- Outside: E = Q/(4πε₀r²)
When to Use Gauss’s Law?
Symmetry होने पर Gauss’s law बहुत powerful है!
Use करें जब:
- Spherical symmetry
- Cylindrical symmetry
- Planar symmetry
Use न करें जब:
- Irregular shapes
- No clear symmetry
Problem Solving Techniques: Master बनने का तरीका!
Step-by-Step Approach
Step 1: Analyze the Problem
- कौन से charges हैं?
- कौन सी quantities find करनी हैं?
- कौन सा law/principle use करना है?
Step 2: Draw the Diagram
- Clear diagram बनाएं
- Coordinate system establish करें
- Directions mark करें
Step 3: Apply Physics Principles
- Relevant formulas identify करें
- Symmetries look करें
- Vector nature को consider करें
Step 4: Mathematical Solution
- Carefully calculate करें
- Units check करें
- Answer की reasonableness verify करें
Common Problem Types
Type 1: Force Calculation
- Coulomb’s law direct application
- Vector addition for multiple charges
Type 2: Field Calculation
- Point charge field formula
- Superposition principle
Type 3: Dipole Problems
- Moment calculation
- Field at different positions
- Torque in external field
Type 4: Gauss’s Law Applications
- Flux calculations
- Field using symmetry arguments
Competitive Exam Preparation Tips
JEE Main/Advanced के लिए
High-Weightage Topics:
- Coulomb’s law और superposition
- Electric field calculations
- Dipole moment और field
- Gauss’s law applications
- Field line properties
NEET के लिए
Focus Areas:
- Basic concepts और definitions
- Coulomb’s law numerical problems
- Electric field direction
- Dipole properties
- Conceptual questions
Quick Revision Formula Sheet
Key Formulas:
* Coulomb's Law: F = kq₁q₂/r²
* Electric Field: E = F/q₀ = kQ/r²
* Dipole Moment: p = qd
* Dipole Field (axial): E = 2kp/r³
* Dipole Field (equatorial): E = kp/r³
* Gauss's Law: ∮E⃗⋅dA⃗ = Q/ε₀Memory Tricks
Mnemonics:
- “Positive से Positive भागता है” (Like charges repel)
- “Field Lines का Golden Rule: + से – की तरफ”
- “Gauss Uncle का कहना: Flux = Charge/ε₀”
Laboratory Experiments और Practical Applications
Important Experiments
1. Coulomb’s Law Verification
- Torsion balance का use
- Force measurement technique
- Data analysis methods
2. Electric Field Mapping
- Conducting paper method
- Equipotential lines plotting
- Field line visualization
3. Charge Distribution Study
- Van de Graaff generator
- Electroscope experiments
- Charging by induction
Modern Applications
1. Technology में:
- Capacitive touch screens
- Laser printers (electrostatic printing)
- Air purifiers (electrostatic precipitation)
- Photocopying machines
2. Medical Field में:
- ECG (heart’s electrical activity)
- Defibrillators
- Electric shock therapy
- Nerve stimulation devices
3. Industrial Applications:
- Paint spraying (electrostatic)
- Dust collection
- Semiconductor manufacturing
- Particle accelerators
Career Connections: Future की Possibilities
Engineering Fields
Electrical Engineering:
- Power systems design
- Electronic circuit analysis
- Electromagnetic compatibility
Electronics Engineering:
- Semiconductor device physics
- Integrated circuit design
- Signal processing systems
Research Opportunities
Physics Research:
- Particle physics experiments
- Plasma physics studies
- Condensed matter research
- Quantum electrodynamics
Applied Sciences:
- Materials science
- Nanotechnology research
- Renewable energy systems
- Medical physics
Emerging Technologies
Future Scope:
- Electric vehicles technology
- Wireless power transfer
- Quantum computing
- Advanced medical devices
- Space technology applications
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: विद्युत आवेश कैसे उत्पन्न होता है?
Answer: आवेश उत्पन्न नहीं होता, बल्कि transfer होता है। जब दो objects रगड़े जाते हैं, electrons एक से दूसरे में transfer हो जाते हैं।
Q2: क्या electric field lines intersect कर सकती हैं?
Answer: नहीं! अगर field lines intersect करें तो एक point पर दो directions होंगी, जो impossible है।
Q3: Coulomb’s law और Newton’s law में क्या similarity है?
Answer: दोनों inverse square laws हैं। Distance के साथ force 1/r² के अनुपात में decrease होती है।
Q4: Electric field का SI unit क्या है?
Answer: N/C (Newton per Coulomb) या V/m (Volt per meter)
Q5: Dipole moment का direction क्या होता है?
Answer: Negative charge से positive charge की तरफ (conventional definition)
Quick Reference Tables
Important Constants
| Quantity | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elementary charge | e | 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ | C |
| Coulomb constant | k | 9 × 10⁹ | Nm²/C² |
| Permittivity of free space | ε₀ | 8.85 × 10⁻¹² | C²/Nm² |
Common Charge Values
| Object | Typical Charge |
|---|---|
| Electron | -1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ C |
| Proton | +1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ C |
| Lightning | ~10 C |
| Static electricity | ~10⁻⁶ C |
Motivational Corner
“भौतिकी सिर्फ formulas नहीं है – यह प्रकृति की भाषा है!”
Success Stories:
- Michael Faraday: बिना formal education के electromagnetic theory के founder बने
- Benjamin Franklin: Lightning experiments से electricity की understanding बढ़ाई
- Charles Coulomb: Simple torsion balance से fundamental law discover किया
आपका Physics Journey:
- Day 1-7: Basic concepts clear करें
- Day 8-15: Problem solving practice करें
- Day 16-21: Previous year questions solve करें
- Day 22-30: Revision और mock tests
Remember: “हर great physicist भी कभी beginner था। आपकी curiosity ही आपकी सबसे बड़ी strength है!”
Additional Resources
Recommended Books
- NCERT Physics Class 12 – Foundation के लिए
- Concepts of Physics by H.C. Verma – Deep understanding
- Fundamentals of Physics by Resnick Halliday Krane – Advanced level
Online Resources
- Khan Academy Physics – Visual learning
- Physics Wallah – Hindi explanations
- Unacademy JEE – Competitive exam prep
- BYJU’S Learning App – Interactive content
Practice Platforms
- Toppr – Adaptive practice
- Vedantu – Live classes
- Embibe – AI-powered analysis
- Doubtnut – Instant doubt solving
Conclusion: आपका Physics Adventure शुरू हो चुका है!
दोस्तों, आज हमने Electric Charges and Fields की amazing journey complete की है! इस chapter में हमने सीखा:
✅ विद्युत आवेश की fundamental nature
✅ Coulomb’s law का powerful application
✅ Electric field की mathematical beauty
✅ Field lines की visual elegance
✅ Dipole की practical importance
✅ Gauss’s law की symmetric power
याद रखिए: Physics डरने की चीज़ नहीं है – यह तो प्रकृति के secrets को unlock करने का magical key है! जब आप mobile phone use करते हैं, LED lights जलाते हैं, या computer operate करते हैं – हर जगह electric charges का role है।
आपकी सफलता के लिए Final Tips:
- Daily practice करें – consistency is key
- Concepts को visualize करें – imagination की power use करें
- Real-life connections बनाएं – physics everywhere है
- Mistakes से डरें नहीं – learning process का हिस्सा हैं
- Questions पूछते रहें – curiosity never stops!
यह comprehensive guide आपको Class 12 Physics के Electric Charges and Fields chapter में excellence achieve करने में मदद करेगा। Regular practice और conceptual clarity के साथ आप definitely success पाएंगे!
इसे भी पढ़ें –


1 thought on “विद्युत आवेश और क्षेत्र – कक्षा 12 भौतिकी अध्याय 1 नोट्स (CBSE 2025-26): रहस्यों से भरी दुनिया का सफर!”